Early on in her training, the mare was labeled as a hot off-track Thoroughbred, but was that really her M.O.? Underneath the young mare’s frightening antics was a kind, gentle soul. Through exams, lameness evaluations and radiographs, vets at last pinpointed what was causing her “misbehavior”: a fractured, mis-healed vertebrae that inflicted pain from bone-on-bone contact and osteoarthritis (OA).

Allday has been the lameness specialist for equine legends that include Triple Crown race winners, 29 Breeders’ Cup race winners, and five Thoroughbred Horses of the Year—including legendary racehorses A.P. Indy and Cigar—among other elites, such as World Equestrian Games jumpers. In addition to being a top sport horse veterinarian, Allday has also founded and developed a line of joint supplements.
1. What is equine osteoarthritis?
Sometimes hidden and other times obvious, equine osteoarthritis (OA) is a condition that impacts horses regardless of age, breed or discipline. It’s estimated that OA is responsible for up to 60 percent of all lameness in horses, according to the American Association of Equine Practitioners (AAEP).
Also referred to as equine degenerative joint disease, OA is a chronic disease-causing degeneration of the joints and resulting in pain, inflammation and reduced flexibility and range of motion. To understand OA, it’s important to understand the three different types of joints horses have:
1. Synovial joints: These allow different degrees of movement and rotation, acting as a hinge for the primary mode of flexion and extension. Examples include fetlocks, knees and hocks.
2. Fibrous joints: These do not allow for movement between the bones, such as the joints between bones of the skull.
3. Cartilaginous joints: These connect bones with cartilage, allowing limited movement and shock absorption, like the joints between the vertebrae of your horse’s spine.
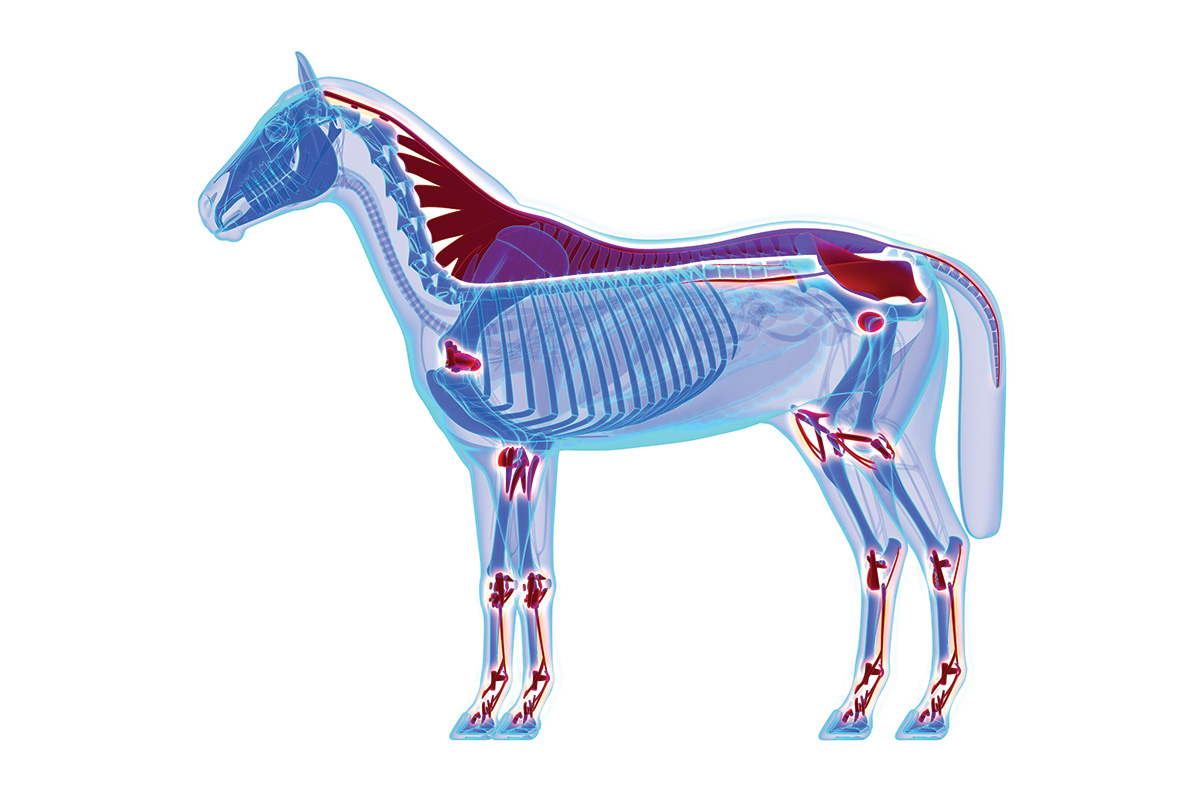
Osteoarthritis can occur in synovial and cartilaginous joints, and it’s a common condition horses can experience.
“Osteoarthritis is ubiquitous in all mammals, and progressive as a rule,” says Allday. “It can occur anywhere on the horse: in their hips, hocks, stifles, knees, fetlocks and other joints.”
2. What causes equine osteoarthritis?
You may have wondered if different equine sports affect specific joints. Although any horse in any discipline can be affected by OA, there are common themes and joint problems that occur in the varying equine sports.
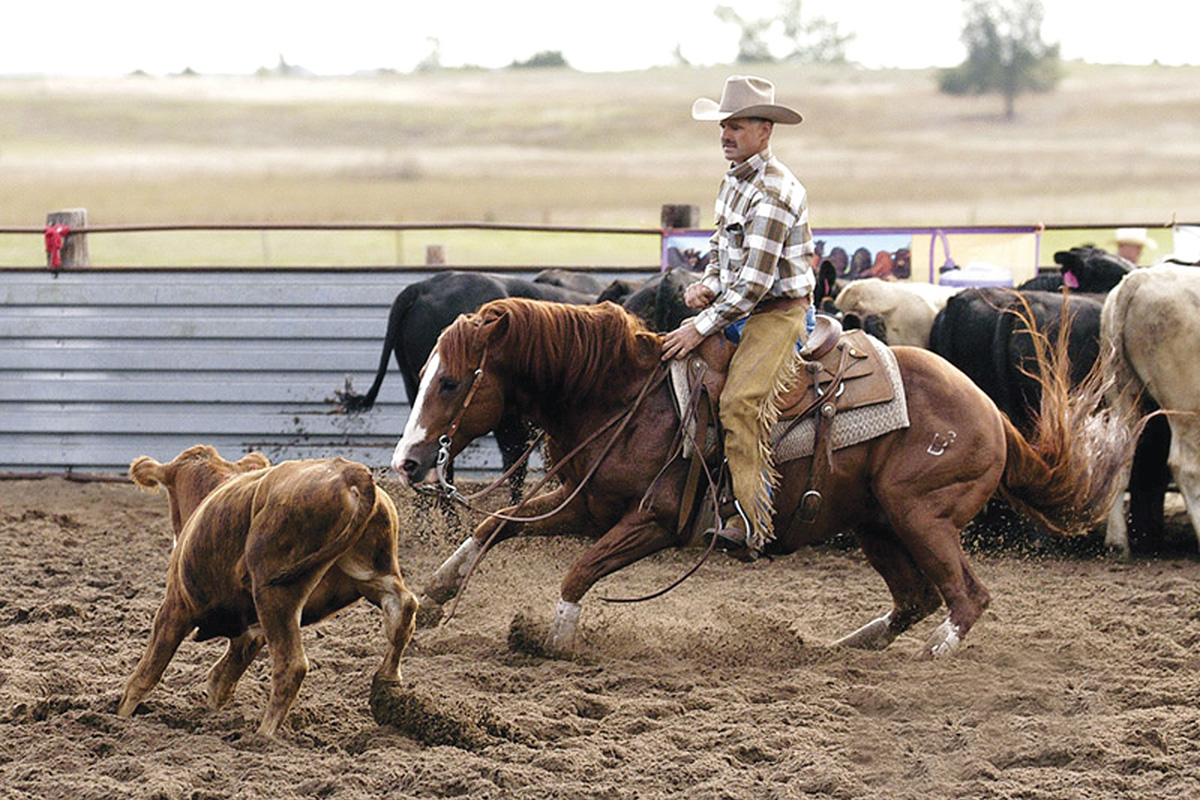

For instance, cutting and reining have greater impact on the hocks and stifles, causing horses to have heightened OA risk to these joints. And jumpers are more likely to have front-limb lameness in the coffin or fetlock joints. The bottom line is that any joint that is more significantly used on a horse increases its likelihood for developing OA.
3. Can osteoarthritis be prevented?
To help avoid joint health problems, you need to get ahead of what problems can—and unfortunately, likely will—arise due to a horse’s conformation flaws, stabling or training environments and everyday injury risks.
“Whether a racehorse, dressage horse, cutting horse or a barrel horse, by maintaining things preventatively and staying a step ahead of potential problems before they become a major issue, you can help ensure your equine partner’s performance,” says Allday.

You can help prevent equine joint health problems by:
◆ Offering quality nutrition for strong bones and healthy cartilage.
◆ Prioritizing hoof care and keeping horses on a regular trim schedule.
◆ Keeping horses at optimum weight and avoiding obesity, which stresses the joints.
◆ Riding on softer footing and limiting work on hard surfaces.
◆ Incorporating joint supplements to help maintain their joints and cartilage.
4. How is osteoarthritis diagnosed?
Allday assures us that as the No. 1 human in your horse’s life, you are the best diagnostician of any changes in your horse’s joint health.
“This is simply because you know your horse,” he says. “I don’t have a crystal ball. When I go look at a horse, I’m taking a snapshot of that moment, while you have known the horse for days and years—sometimes, his entire life—before I got there that day.”
Every time you’re grooming or tacking up for a ride, check your horse for symmetry: If you fear one side is larger than the other, you can just compare it to his opposite side.
Give your horse a proper once-over: Rub his back and palpate it, checking for soreness.
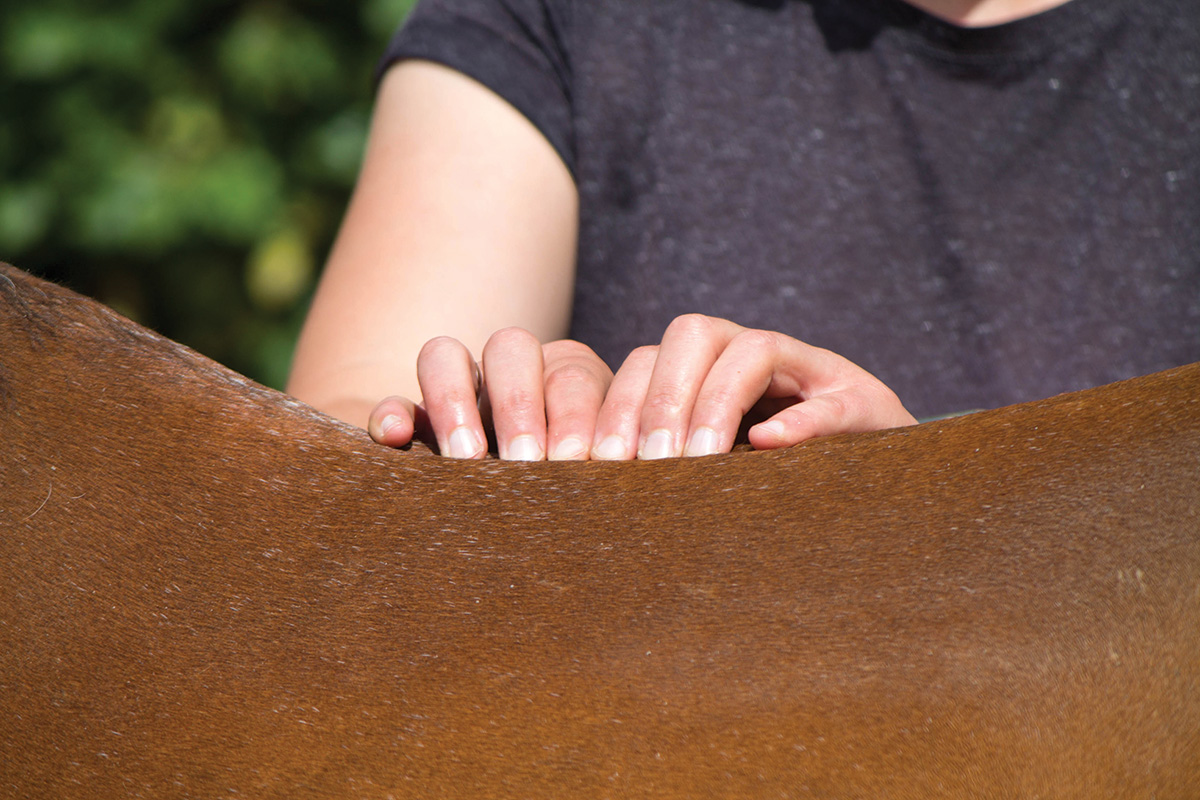

When you pick up his hind leg, check the hock for any fluid. This daily interaction with your horse, coupled with knowledge of his particular history, will be invaluable to your veterinarian when diagnosing any joint problems.
Should your veterinarian suspect joint problems, it’s likely he or she will perform a routine lameness evaluation. According to the American Association of Equine Practitioners, this includes summarizing the horse’s medical history; a visual appraisal of the horse at rest; a thorough, hands-on examination, including palpating the horse’s muscles, joints, bones and tendons for any heat or swelling; an evaluation of your horse’s three gaits in motion; and a joint flexion test.

“Every horse deserves a full and thorough veterinary examination,” says Allday. “It’s not just a choice—it’s a necessity to help maintain these equine athletes and keep them at their best.”
In addition to lameness evaluations, diagnosis of OA can also involve diagnostics such as:
◆ Radiographs
◆ Fluoroscopy
◆ Nuclear scintigraphy
◆ CT
◆ MRI
◆ Nerve and joint blocks
◆ Ultrasound
◆ Thermography
5. Is equine osteoarthritis curable?
While there is, unfortunately, no definitive cure for OA in horses, the pain and inflammation associated with it can be treated. Prevention, along with early diagnosis and treatment, is critical to keep the condition from progressing.
“OA isn’t the end of their career, but it’s certainly something you have to be on top of, address rapidly and maintain routinely,” says Allday. “You have to remember that osteoarthritis is progressive, and as it gets worse as the horse gets older, you’ll need to be very proactive. You may even have to go to anti-inflammatories to maintain a horse’s athletic career.”
6. What are treatment options?
Treatment for equine OA focuses on alleviating pain and inflammation in the joint, allowing horses to have improved mobility. For horses diagnosed with osteoarthritis, veterinarians may recommend prescription medications, like Equioxx, Adequan I.M., Legend or Surpass Topical.
Should OA be diagnosed, your veterinarian will work closely with you on joint health supplements to prevent further progression of joint damage, as well as anti-inflammatory treatments available to manage the pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis.
Allday recalls a conversation he had with Allen Paulson, founder of Gulfstream Aerospace and renowned owner of more than 100 graded stakes race winners. Paulson’s horse was the favorite for the Kentucky Derby, but due to a joint injury, he was scratched.
“I told him, ‘A horse isn’t like the planes you build—you have to go with the original equipment.’ And it’s true—you can’t put a horse up on a rack and switch in a new part. Taking care of their original equipment is the epitome of how you can preventatively maintain your horse throughout his career.”
What to Look ForOsteoarthritis (OA) is common, and every horse is at risk, no matter his age or discipline. Here are some of the most common causes and clinical signs. Causes: Clinical Signs: Quick Tip: |






